
Bison Hunting in Alaska
Looking to go bison hunting in Alaska? Definitely check out the Alaska Department of Fish and Game website for all the current information you need. Bison hunting is a popular activity in Alaska, with thousands of hunters applying for permits yearly. The state is home to four herds of plains bison, totaling about 900 animals, with the largest herd located near Delta Junction. Hunting is used to manage the size of these herds, making bison hunts among the most popular drawing hunts in the state. If you’re up for the challenge, these majestic animals provide an exciting and rewarding hunting experience.
Understanding Bison
Bison, or American buffalo, have a rich history in Alaska. Let’s explore the history, physical characteristics, behavior, and habitat of bison to gain a better understanding of this iconic species. We will also delve into the hunting practices, management, regulations, and harvest reporting related to bison in Alaska. If you’re interested in bison hunting or simply want to learn more about these magnificent animals, keep reading!
History of Bison in Alaska
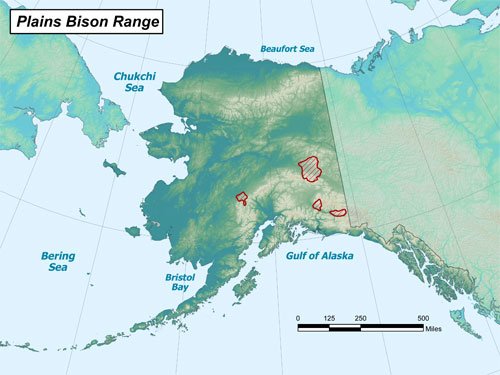
In Alaska, bison have been present since the late 1920s when 23 plains bison were introduced to the Delta River area in the state’s Interior. These plains bison, a subspecies of American bison, were translocated from the National Bison Range in Montana. Over the next few decades, the herd grew to about 400 animals, and hunting of bison began in the 1950s. Today, there are four bison herds in Alaska, totaling around 900 animals. The largest herd is located near Delta Junction, and smaller herds have been established in the Farewell, Chitina River, and Copper River areas.
Physical Characteristics of Bison
Plains bison are the smaller subspecies of American bison found in North America. A full-grown bull stands about 6 feet (1.8 meters) at the shoulder, can be up to 10 feet (3.3 meters) long, and may weigh more than a ton (907 kilograms). Full-grown cows are smaller but can still weigh over 1,200 pounds (544 kilograms). The dressed weight of a 2,000-pound (907-kilogram) bison is approximately 1,200 pounds (544 kilograms), and an animal of this size can yield around 680 pounds (308 kilograms) of meat. Bison may appear clumsy while feeding, but they are actually fast, agile, and tireless runners.
Behavior and Habitat of Bison
Bison are grazing animals and can be found along rivers, in recently burned areas, and in sedge potholes in Alaska. They mainly feed on various grasses and forbs, such as vetch, which is a favored summer food found on gravel bars. They also consume sedges, silverberry, willow, and ground birch. Bison are migratory animals with seasonal movement patterns. They do not remain in single herds but scatter alone or in groups of up to 50 animals or more. In the Delta Junction area, they migrate up the Delta River corridor in early spring to secluded meadows where they calve. Around August, they travel back downstream, eventually moving onto the Delta Junction Bison Range. In late fall, they move onto area farms and state lands where they remain throughout the winter.
Diet and Migration patterns of Bison
Bison primarily feed on various grasses and forbs, such as vetch, sedges, silverberry, willow, and ground birch. They can be found grazing along rivers, in recently burned areas, and in sedge potholes in Alaska. Their diet changes seasonally, and they rely on different food sources throughout the year.
Bison are migratory animals and exhibit seasonal movement patterns. In the Delta Junction area, for example, they migrate up the Delta River corridor in early spring to secluded meadows where they calve. Around August, they travel back downstream, eventually moving onto the Delta Junction Bison Range. In late fall, they move onto area farms and state lands where they remain throughout the winter.
Bison Species in Alaska
Alaska is home to two species of bison: plains bison and wood bison. Let’s take a closer look at each of these species.
Plains Bison
Plains bison (Bison bison bison) are a subspecies of American bison and are an introduced, rather than native, species in Alaska. They were translocated from the National Bison Range in Montana to the Delta River area in the state’s Interior in 1928. The plains bison herd in Alaska has grown to approximately 900 animals, making it the largest bison species population in the state.
Wood Bison
Wood bison (Bison bison athabascae) are a native bison species that were extirpated from Alaska in the 1800s. However, efforts have been made to reintroduce wood bison to the state. These reintroduced wood bison herds are still in the early stages of establishment, but they hold promise for future hunting opportunities in Alaska.
Bison Population and Distribution in Alaska
Understanding the size, growth, and distribution of bison herds in Alaska is essential for effective management and conservation of the species.
Size and Growth of Bison Herds
In Alaska, there are currently four bison herds: the Delta herd, the Farewell herd, the Chitina River herd, and the Copper River herd. The largest herd is the Delta herd, which consists of approximately 700 to 800 animals. The Farewell, Chitina River, and Copper River herds are smaller and have been established through translocation efforts.
The population of bison in Alaska has seen steady growth over the years. From the initial introduction of 23 plains bison in the late 1920s, the herd has grown to approximately 900 animals. Management practices, including controlled hunting, play a crucial role in maintaining the population at sustainable levels.
Herd Locations and Ranges
The main bison herds in Alaska are located in specific areas. The Delta herd’s primary range is near Delta Junction, while the Farewell, Chitina River, and Copper River herds were established through translocation efforts from the Delta herd. These herds have specific migration patterns and ranges, but they may also scatter and move alone or in smaller groups.
Bison Hunting practices in Alaska
Hunting bison in Alaska is an exciting and challenging endeavor that requires specific tools, equipment, and adherence to ethical hunting practices. Let’s explore some key aspects of bison hunting in the state.
Tools and Equipment for Bison Hunting
When it comes to hunting bison in Alaska, hunters need to make sure they have the appropriate tools and equipment. This includes a firearm suitable for taking down a large animal like a bison, such as a high-powered rifle. Ammo selection is important to ensure clean and ethical kills, and hunters should consider using heavy, controlled-expansion bullets. Other essential equipment includes binoculars, proper clothing and footwear for harsh weather conditions, a good backpack, a game meat pack, and processing equipment.
Hunting Ethics and Norms
Ethical hunting practices are crucial when hunting bison in Alaska. This involves respecting the animals and the land, hunting within legal and regulatory frameworks, and ensuring sustainable hunting practices. It is essential to follow all hunting regulations, including bag limits and seasonal restrictions, to ensure the conservation of the bison population. Hunters must also practice responsible and safe firearm handling and conduct themselves in an ethical manner throughout the hunting experience.
Damage and Disease Control
Hunting also plays a role in managing bison populations to mitigate potential damage and disease risks. Overpopulation of bison can lead to overgrazing and damage to important habitats, putting other wildlife and ecosystems at risk. Bison hunting helps manage herd sizes, ensuring a healthy balance between the bison population, other wildlife, and the environment.
Additionally, hunting can help control the transmission of diseases among bison, preventing the spread of pathogens that could potentially impact the health of the herd. Appropriate disease monitoring and control measures are implemented to protect the overall population and maintain healthy bison herds in Alaska.
Hunting Management in Alaska
Effective management of bison hunting in Alaska requires clear objectives and strategies to ensure sustainable populations and a balance with habitat and other wildlife.
Management Objectives and Strategies
The management objectives for bison hunting in Alaska focus on maintaining sustainable populations, preventing damage to habitats, and minimizing disease risks. Strategies involve setting appropriate hunting seasons, bag limits, and drawing permit systems to control the number of animals harvested. Collaborative efforts between state wildlife agencies, biologists, stakeholders, and the local community are essential in managing bison populations effectively.
Role of Hunting in Bison Management
Hunting plays a vital role in managing bison populations in Alaska. By allowing controlled hunting, state wildlife agencies can regulate herd sizes, prevent habitat degradation, and reduce the risk of diseases among bison. Hunting also provides opportunities for local communities and individuals to engage in subsistence practices and maintain cultural traditions.
Bison Hunting Regulations in Alaska
Understanding the regulations and requirements for hunting bison in Alaska is crucial for hunters. Here are some key aspects to consider.
Obtaining Hunting Permits
To hunt bison in Alaska, hunters must obtain the necessary hunting permits. These permits are typically issued through a drawing system, and the application process involves submitting applications and paying applicable fees within specific timeframes. Hunters should review the application process, eligibility requirements, and deadlines specified by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game.
Bison Hunting Seasons
Bison hunting seasons are set by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game and are subject to change based on population dynamics and conservation objectives. It is essential for hunters to stay updated on the latest hunting season dates, bag limits, and any specific restrictions in the areas they plan to hunt.
Legal Requirements and Restrictions
Hunters must adhere to all relevant legal requirements and restrictions when hunting bison in Alaska. This includes possessing a valid hunting license, following specific hunting regulations, abiding by bag limits, and reporting harvested animals as required by law. It is the responsibility of hunters to familiarize themselves with the specific legal requirements and restrictions before engaging in bison hunting activities.
Drawing Hunts for Bison in Alaska
Drawing hunts provide opportunities for hunters to participate in controlled hunts for specific species, including bison. Let’s explore what drawing hunts are and the popularity and application processes for bison drawing hunts in Alaska.
What are Drawing Hunts?
Drawing hunts, also known as controlled hunts, are a management tool used by state wildlife agencies to regulate hunting opportunities for specific species. These hunts involve a lottery system where hunters apply for permits, and a limited number of permits are issued through random selection or preference point systems. Drawing hunts aim to distribute hunting opportunities fairly and manage populations effectively.
Popularity and Application for Bison Drawing Hunts
Bison drawing hunts in Alaska are highly popular. Each year, thousands of hunters apply for a limited number of permits, resulting in a competitive application process. For example, the Delta bison hunt, one of the most sought-after drawing hunts in Alaska, receives approximately 15,000 applications for about 100 permits annually. The popularity of bison drawing hunts reflects the interest and fascination surrounding hunting this iconic species.
Bison Harvest Reporting
Reporting the harvest of bison is a crucial component of responsible hunting and effective wildlife management. Let’s explore the reporting requirements and the importance of harvest statistics.
Reporting Requirements
Hunters are required by law to report their bison harvest within a specified timeframe. The reporting requirements may vary depending on the specific hunting unit and regulations set by the Alaska Department of Fish and Game. Reporting helps wildlife managers collect accurate data about harvest rates, population trends, and the overall health of bison herds.
Harvest Statistics
Harvest statistics play a vital role in wildlife management and decision-making processes. By analyzing harvest data, wildlife biologists can assess population dynamics, monitor the effectiveness of management strategies, and make informed decisions about hunting seasons, bag limits, and conservation efforts. Accurate and timely reporting from hunters is essential for maintaining reliable harvest statistics.
Learning More About Bison in Alaska
For those interested in learning more about bison in Alaska, various resources provide valuable information on bison conservation, research, and general knowledge about the species.
Resources for Information
The Alaska Department of Fish and Game is an excellent resource for information on bison in Alaska. Their website provides comprehensive information about bison hunting regulations, hunting permits, herd management, and conservation efforts. In addition to government sources, scientific journals, wildlife organizations, and educational institutions may offer valuable insights into the biology, behavior, and ecology of bison.
Bison Conservation and Research
Conservation and research efforts play an essential role in securing the future of bison populations in Alaska. Scientists and wildlife managers continually study bison populations to better understand their behavior, habitat requirements, and the impact of hunting practices on their populations. Conservation initiatives focus on maintaining healthy bison herds, protecting their habitats, and promoting sustainable hunting practices.
Additional Opportunities for Bison Hunting
While plains bison currently offer hunting opportunities in Alaska, the reintroduction of wood bison holds promise for future hunts. Let’s explore potential future hunts and non-hunting alternatives related to bison in the state.
Potential Future Hunts
Wood bison, a native bison species extirpated from Alaska in the 1800s, have been reintroduced to the state. These reintroduced wood bison herds are still in the early stages of establishment, but they hold promise for future hunting opportunities. As populations continue to stabilize, wildlife managers may consider introducing controlled hunting seasons for wood bison.
Non-Hunting Alternatives
For individuals interested in bison but not hunting, Alaska offers various non-hunting alternatives to observe and appreciate these majestic animals. Wildlife viewing opportunities, guided tours, educational programs, and photography workshops can provide unique and memorable experiences with bison in their natural habitat.
In conclusion, understanding bison in Alaska is essential for anyone interested in hunting these iconic creatures or learning more about their biology, behavior, and conservation. By exploring the history, physical characteristics, behavior, habitat, hunting practices, management, regulations, and reporting requirements related to bison, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of this magnificent species and its role in Alaska’s wildlife ecosystem.